Hey guys!
Today we ‘re gonna see how to create a Menu with icon
items, which on click, fire a respective to them message. What
differentiates this article from other similars, is that we ‘re using
the latest Android APIs, where Menus are manipulated differently.
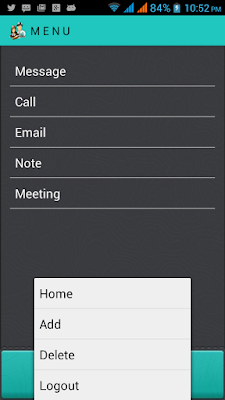
Having created an Android project, using the latest platform, gives us by default a menu layout, as we can see:
For those who are more curious about what this contains, have a look at the Screen shots of this program
:
1. Option Menu. 2.Context Menu

menu.xml
creating the menu item in menu.xml file
<menu
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:context="com.allmenodemo.MainActivity" >
<item
android:id="@+id/home"
android:orderInCategory="100"
android:title="@string/home"
android:icon="@drawable/home"
/>
<item
android:id="@+id/add"
android:orderInCategory="100"
android:title="@string/add"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_action_add"
/>
<item
android:id="@+id/delete"
android:orderInCategory="100"
android:title="@string/delete"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_delete"
/>
<item
android:id="@+id/logout"
android:orderInCategory="100"
android:title="@string/logout"
android:icon="@drawable/logout"
/>
</menu>
Let’s pretend that we don’t really know anything about
menus, so when running the app on our emulator, if we press the hardware “Menu” button, we should get something like Settings and more.
here menu tag defines menu and item tag defines elements or items which will shown on option menu button.
Creating a custom
menu in Android is very easy, Regarding an
item, we actually need to define 3 properties:
- An
id,
which is useful to handle the action that we want our menu option to
implement, when clicked. This can be done through a Java class.
- An
icon, which has to lie under the drawable.
- A
title, which is the displayed text in our menu item; this is about the title
attribute we already know: it can be manipulated with both the
“hardcoded” way and through the stored strings of our app.
lets move to the Java class for getting this things work.
before start up this code I must tell you one thing that I am implementing all types of android menu in separate section so please be careful while coping this code in your eclipse project.
I am doing this class for :
- Option Menu.
- Context Menu.
MainActivity.java
package com.allmenudemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ContextMenu;
import android.view.ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuInflater;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity{
//In this example I am creating both Menus: i.e.
//1.Option Menu.
//2.Context Menu.
ListView lv;
//For context menu I am creating Simple ListView, So I can make
//long press on item to get context menu.
String[] data = new String[] { "Message", "Call", "Email", "Note",
"Meeting" };
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView1);
ArrayAdapter ad = new ArrayAdapter(getApplicationContext(),
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, data);
lv.setAdapter(ad);
registerForContextMenu(lv);
}
//Context Menu-------------------------------------
@Override
public void onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu menu, View v,
ContextMenuInfo menuInfo) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
menu.setHeaderTitle("Select Options");
menu.add(0, v.getId(), 0, "Msg");
menu.add(0, v.getId(), 0, "Call");
menu.add(0, v.getId(), 0, "Email");
menu.add(0, v.getId(), 0, "Note");
menu.add(0, v.getId(), 0, "Meeting");
super.onCreateContextMenu(menu, v, menuInfo);
}
@Override
public boolean onContextItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (item.getTitle() == "Msg") {
Intent i = new Intent(MainActivity.this, PopupDemo.class);
startActivity(i);
finish();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Msg ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else if (item.getTitle() == "Call") {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Call ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else if (item.getTitle() == "Email") {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Email ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else if (item.getTitle() == "Note") {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Note ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else if (item.getTitle() == "Meeting") {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Meeting ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
return false;
}
//Option Menu----------------------------------------
//here I am creating options menu from menu.xml file.
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
MenuInflater m = getMenuInflater();
m.inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.home:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Home Option ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
case R.id.add:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Add Option ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
case R.id.delete:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Delete Option ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
case R.id.logout:
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "U selected Logout Option ",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
break;
default:
break;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
@Override
public void onBackPressed() {
moveTaskToBack(true);
}
// Before 2.0
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) {
moveTaskToBack(true);
return true;
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
}
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.allmenudemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="20" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/studentprofile"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Example" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:screenOrientation="portrait" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Now, Run The Application.
Stay tune for next Session Happy codding :)